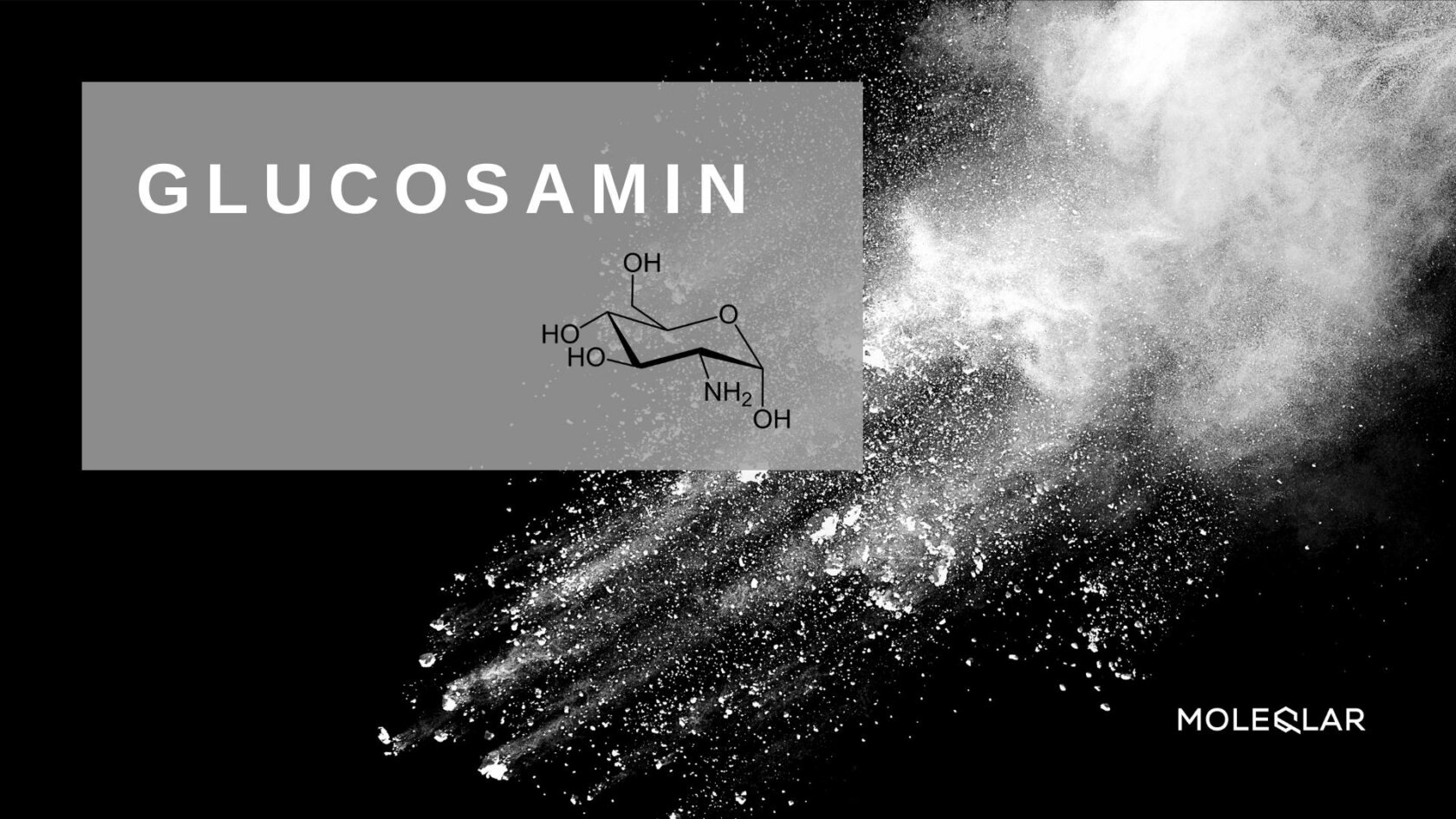
Hyaluron, or hyaluronic acid, is familiar to many from plastic surgery, where the substance has long been used as a "wrinkle filler" for the skin. The molecule occurs naturally in our body - we can even produce it ourselves to a certain extent. However, as we age, the amount of hyaluronic acid in our bodies decreases, resulting in reduced skin elasticity. Some studies have shown that a regular supply of hyaluron can reduce the depth of wrinkles. Learn more about the fascinating molecule hyaluron and what benefits it has for you.
Occurrence of hyaluron
The name hyaluronic acid goes back to its discoverer Karl Meyer. In the 1930s, Meyer isolated a substance consisting of many disacharides and uronic acids from the vitreous humour of bovine eyes for the first time. The ancient Greek word for glass is "hyalos" and thus he named the newly discovered substance hyaluronic acid. Hyaluron is the abbreviation of the word.
In our body there is a total of about 15 grams of hyaluronic acid, distributed among other things in our joints, connective tissue, the vitreous body of the eye and in the skin. About half of all hyaluronic acid is found in the skin, both in the upper epidermis and in the deeper dermis.
Here are a few more impressive numbers:
- The hyaluronic acid content in the skin of a 75-year-old is only about a quarter of that of a 19-year-old person!
- Your body synthesizes about 5g of hyaluronic acid per day, and the same amount is broken down. So about a third of the total amount of hyaluronic acid in your body is broken down and rebuilt every day.
What does hyaluronic acid do?
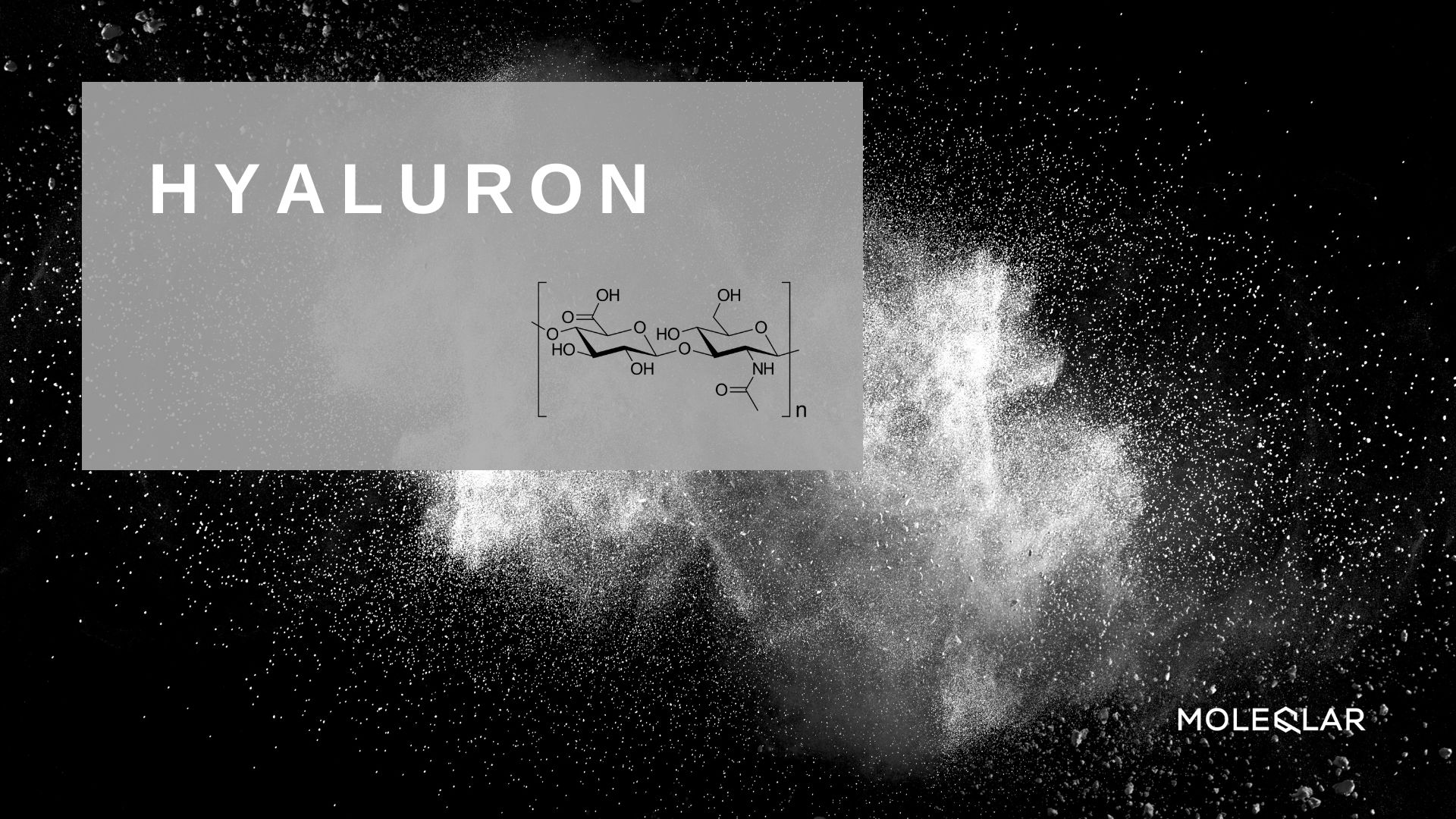
To understand the role of hyaluronic acid in our body, we need to take a closer look at its molecular structure. Hyaluronic acid consists of a string of two-sugar molecules, so-called disaccharides. The disaccharide molecules are modified glucose building blocks with the complicated names D-glucuronic acid and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine. The changes allow the individual two-sugars to be linked together like a chain. This is chemically called polymers. This structure makes it possible for hyaluron to bind a great deal of water .
Depending on how many two-sugars are linked together, molecules of different weight are obtained. A rough distinction is made between light, also called low-molecular hyaluron (NMW), and heavy, so-called high-molecular hyaluron (HMW).
This distinction is important because the two molecules have different properties.
High Molecular Weight Hyaluron (HMW)
High-molecular hyaluron is said to exist from a weight of106 Dalton. This is approximately 100 kilodaltons (kDA). High-molecular-weight hyaluron, as found in MoleQlar Hyaluron is found in joint cartilage and synovial fluid as a "lubricant". In addition, some studies have shown that it has a positive effect on wound healing. It supports connective tissue and reduces inflammation in the body via interaction with surface molecules of our defense cells.
In addition, some double-blind, placebo-controlled studies (highest level of evidence) demonstrated that wrinkle depth was significantly reduced after 28 days of oral intake of high molecular weight hyaluronan.
One gram of hyaluronic acid can bind about 6 liters of water. The vitreous body of our eye consists of about 98% water. The remaining two percent are hyaluron and collagen fibers.
Low molecular weight hyaluron (NMW)
Low-molecular hyaluron was also able to reduce wrinkle depth in some studies - however, it was not as effective as high-molecular hyaluron. Under low molecular weight hyaluron, proinflammatory (pro-inflammatory) signals were more likely to be observed.
In certain diseases, bronchial asthma, pulmonary fibrosis and arterial hypertension, endogenous high molecular weight hyaluron is converted into low molecular weight hyaluron. Studies have shown that this shift to more NMW, promotes an increased inflammatory response.
Hyaluron in science and research
Hyaluron is used in many areas of medicine due to its unique biological and chemical properties. Here are some examples:
- as a "carrier substance" in medicinal products.
- as a topical application in wound healing
- in eye surgery to protect the eye
- as a "lubricant" in the joint
- As an ingredient in nasal sprays to reduce dryness.
There are many other areas in which hyaluron is used. For example, one area of research is the use of hyaluronic acid as a "carrier" molecule for anti-cancer drugs. It has been shown that some tumors over express the receptor CD44. Hyaluronic acid can bind to this receptor, making it an interesting molecule to develop targeted therapies.
Did you know?
Hyaluronic acid is a very versatile molecule that plays an important role in ageing research. It probably has a positive effect on some of the hallmarks of ageing. This is one of the reasons why we have developed our innovative MoleQlar ONE we also use hyaluronic acid as an effective ingredient.

How do we absorb hyaluronic acid?
Hyaluron is - as mentioned before - a rather large molecule. Too big to be completely absorbed by our intestines. For this reason, it has long been assumed that a sip substitution of hyaluron can do nothing, after all, the molecule is broken down into smaller pieces in our intestines.
However, this assumption could be disproved. It is true that hyaluron is broken down into smaller fragments in our intestines. However, these fragments find their way into our connective tissue and activate the same signaling pathways there as hyaluron. Additionally, high molecular weight hyaluron is absorbed as a complete molecule through our lymphatic system. In a larger review, the results of several studies were compiled. In doing so, several findings emerged. First, the researchers found that after taking high molecular weight hyaluronic acid daily for at least four weeks, wrinkles reduced and skin hydration improved. Even more exciting, one study showed that orally ingested high-molecular-weight hyaluron is deposited in the connective tissue.
In one study, 60 patients with osteoarthritis of the knee were given 200mg of hyaluron orally for 12 months. The other group received cornstarch. Both groups were given a comparable sports program. After 12 months, the hyaluronan group benefited. It showed a greater reduction in pain, with those under 70 years of age benefiting particularly from daily use.

Hyaluron in the cosmetics industry
Hyaluron has long been known in the cosmetics industry as an additive in creams, serums or gels.
Our skin owes its elasticity and firmness to the connective tissue. The main components are collagen, elastin and hyaluronic acid. Thanks to its water-binding capacity, hyaluronic acid is responsible for the moisture content and therefore indirectly for the firmness of our skin.
As our body produces less and less hyaluron with age and the skin thus loses fluid, the filler substance is lost. We see this when our skin wrinkles. Often our skin is a reflection of our "felt" age. Our largest organ is visible to everyone around us, which is why we want to avoid aging skin as much as possible.
Hyaluron gels promise to compensate for this fluid loss. However, the study situation here is not clear. It is very likely that hyaluron applied to the skin cannot penetrate deep enough into the skin. It rather binds the water on the skin. The only option, besides oral supplementation, is to inject hyaluron into the skin. Depending on the hyaluron used, the effect lasts from 6 to 24 months.
Collagen is the most abundant protein in our skin. As we age, our body reduces collagen synthesis, similar to hyaluronic acid. This also contributes to skin ageing.
According to some studies, glycine, an amino acid that we take in with our food, can promote collagen synthesis and thus, together with hyaluronic acid, prevent premature skin ageing.
So glycine and hyaluron together act on two important aging processes in the skin and can have positive effects on your skin health. Both molecules come together in MoleQlar® Hyaluron are present.
Hyaluronic acid for different skin types: What you should know
There are different types of hyaluronic acid products that are tailored to different skin types.
Dry skin: Hyaluronic acid can help to lock moisture into the skin, relieving dryness and tightness. It is particularly effective when applied to damp skin and sealed with a moisturizing cream.
Oily skin: People with oily skin can also benefit from hyaluronic acid, as it moisturizes without clogging the pores or leaving an oily film on the skin.
Sensitive skin: Hyaluronic acid is very gentle on the skin and can therefore also be used on sensitive skin. It can help to strengthen the skin barrier and minimize irritation.
"Old" skin: As we age, the skin's natural hyaluronic acid content decreases, which can lead to dryness and the formation of wrinkles. Hyaluronic acid products can help to minimize these signs of skin ageing.
Hyaluronic acid in skincare: the current state of science
Hyaluronic acid is a natural component of the body that can be found in many skin care products. It is known for its ability to bind water, thereby hydrating and firming the skin.
Hyaluronic acid can bind moisture: Hyaluronic acid has the ability to bind up to 1000 times its own weight in water. This makes it an excellent moisturizer and helps to keep the skin hydrated and plump.
Hyaluronic acid can strengthen the skin barrier: Through its moisturizing properties, hyaluronic acid can help strengthen the skin barrier, contributing to healthy, resilient skin.
Hyaluronic acid can minimize signs of skin ageing: As we age, the skin's natural hyaluronic acid content decreases, which can lead to dryness and wrinkling. Topical applications of hyaluronic acid can help to reduce these signs of ageing.
Hyaluronic acid is safe for most skin types: Hyaluronic acid is very gentle on the skin and is usually well tolerated, making it a good option for all skin types, including sensitive skin.

Hyaluronic acid vs. other moisturizers: a comparison
Compared to other moisturizing ingredients, hyaluronic acid provides more intense and longer-lasting hydration. It draws water into the skin and holds it there, helping to keep the skin plump and hydrated. In addition, hyaluronic acid is also very gentle on the skin and is generally well tolerated, making it a good option for all skin types.
Other commonly used moisturizing ingredients are glycerin, urea, aloe vera and various oils. Glycerin is another highly hygroscopic ingredient that draws water into the skin and helps to keep it there. Urea is known for its ability to smooth the skin and remove dead skin cells while moisturizing.
Aloe vera is known for its soothing and moisturizing properties and can be particularly beneficial for dry or irritated skin. Oils, such as jojoba oil or argan oil, can also moisturize and help to strengthen the skin barrier.
How to integrate hyaluronic acid into your daily skincare routine
Hyaluronic acid is a powerful moisturizer and can easily be integrated into your daily skincare routine.
Cleanse your face thoroughly: Before applying hyaluronic acid, it is important to cleanse your face to remove excess oil and dirt. This allows the hyaluronic acid to be better absorbed by the skin.
Apply to damp skin: Hyaluronic acid binds moisture and draws it into the skin. Therefore, it is best to apply hyaluronic acid to damp skin to maximize its moisturizing properties.
Seal with a moisturizer: After applying hyaluronic acid, you should always apply a moisturizing cream or lotion. This helps to seal in the moisture and improve the effectiveness of the hyaluronic acid.
Use regularly: For optimal results, you should use hyaluronic acid products regularly. Many experts recommend using them twice a day, once in the morning and once in the evening.
Combine with other ingredients: Hyaluronic acid can be combined well with other ingredients in your skincare routine. For example, combining hyaluronic acid with vitamin C can help to improve the brightness and radiance of the skin.
At MoleQlar, we offer pure, vegan hyaluronic acid in capsule form and in the highest quality.
Hyaluronic acid in food
Hyaluronic acid is found in both animal and plant foods. In animal foods, hyaluronic acid is found primarily in cartilage tissue or in broths prepared from animal bones. Other sources are:
- Fish, such as mackerel or sea bream
- Potatoes
- Green leafy vegetables
- Bananas
- Almonds
- Sweet potatoes
- Cashews
- Tofu
The exact amounts of hyaluronic acid in foods are not well researched. However, a healthy, balanced diet, in addition to sufficient supplementation, can contribute to an increased intake of hyaluronic acid.
How is hyaluron produced?
In the past, hyaluronic acid had to be extracted laboriously from cattle eyes or rooster combs. Since this method is not very sustainable, researchers have come up with other methods.
Nowadays, hyaluronic acid is produced by genetically modified bacteria. In large fermentation plants, pure, vegan hyaluron can thus be obtained. Due to the various filtration processes, the risk of allergies is also lower than with animal products. The end product is also completely free of genetic engineering, because the bacteria are completely removed.
You can also get this pure, vegan form of hyaluronic acid from from MoleQlar® to order. Together with glycine, hyaluronic acid fights at the forefront of your metabolic and skin health!
Summary
Hyaluronic acid is an important component of our body. However, as we age, we gradually lose the ability to produce hyaluronic acid. This results in reduced skin elasticity, wrinkles increase and our "lubricant" in the joints becomes less, leading to more pain.
Supplementation with hyaluronic acid has been found to be safe in many studies. The daily intake of hyaluron can contribute to the fact that your skin has fewer wrinkles and inflammations in the body are reduced. Thus, among other things, you support your largest organ, the skin, from premature aging.
Literature:
-
- Papakonstantinou, Eleni et al. "Hyaluronic acid: A key molecule in skin aging." Dermato-endocrinology vol. 4,3 (2012): 253-8. link
- Lodén, M, and W Wessman. "The influence of a cream containing 20% glycerin and its vehicle on skin barrier properties." International journal of cosmetic science vol. 23,2 (2001): 115-9. link
- Oe, Mariko et al. "Oral hyaluronan relieves wrinkles: a double-blinded, placebo-controlled study over a 12-week period." Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology vol. 10 267-273. 18 Jul. 2017, Link
- Fallacara, Arianna et al. "Hyaluronic Acid in the Third Millennium." Polymers vol. 10,7 701. 25 Jun. 2018, Link
- Bayer, Ilker S. "Hyaluronic Acid and Controlled Release: A Review." Molecules (Basel, Switzerland)vol. 25,11 2649. 6 Jun. 2020, Link
- Li, Peng, and Guoyao Wu. "Roles of dietary glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline in collagen synthesis and animal growth." Amino acids vol. 50.1 (2018): 29-38. link
- Tashiro, Toshiyuki et al. "Oral administration of polymer hyaluronic acid alleviates symptoms of knee osteoarthritis: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study over a 12-month period." TheScientificWorldJournal vol. 2012 (2012): 167928. link
- Michelotti, Angela et al. "Oral intake of a new full-spectrum hyaluronan improves skin profilometry and ageing: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial." European journal of dermatology : EJD vol. 31,6 (2021): 798-805. link
Graphics:
The images were purchased under licence from Canva.